Have you noticed your graphics card’s VRAM usage being unusually high, even when your PC is idle? VRAM standing for Video RAM is a type of memory located on the GPU that holds graphical data needed to display images and video on your monitor.
When your computer is idle, VRAM usage is expected to be low since you aren’t running graphics-intensive apps. But some users notice VRAM usage of 50%, 70%, or even 90%+ when their PC is idle.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover:
- What is VRAM and how it works
- How to check current VRAM usage on your PC
- Common reasons for high VRAM usage when idle
- Solutions to reduce high idle VRAM usage
- Tools to optimize VRAM usage
- How much VRAM you really need
- Whether high idle VRAM usage causes problems
- And more…
By the end of this guide, you’ll have a clear understanding of why your idle VRAM usage might be so high, as well as actionable tips to optimize and reduce it.
What is VRAM?
VRAM stands for Video Random Access Memory. It is a type of memory located on the graphics card or GPU that temporarily stores visual information needed to display images on your monitor.
Both integrated and dedicated GPUs have VRAM.
Integrated graphics – Uses your normal system RAM and allocates some portion of it to act as VRAM. For example, Intel integrated graphics will set aside up to 1.5GB system RAM for VRAM.
Dedicated graphics – Have their own memory chips on board solely for VRAM. For instance, an NVIDIA RTX 3060 Ti has 8GB of GDDR6 memory exclusively for VRAM.
VRAM is extremely fast memory optimized for graphical work. It helps store and manipulate 3D models, textures, pixels and other graphical data quickly so complex 3D scenes can be rendered on screen in real-time.
The more VRAM your GPU has, the higher resolution textures and models it can store, allowing for better overall visuals and graphics performance in games and apps.
How to Check VRAM Usage
Before troubleshooting high VRAM usage, you’ll first want to check how much VRAM is currently being utilized on your PC.
Here are some easy ways to monitor your VRAM usage in real-time:
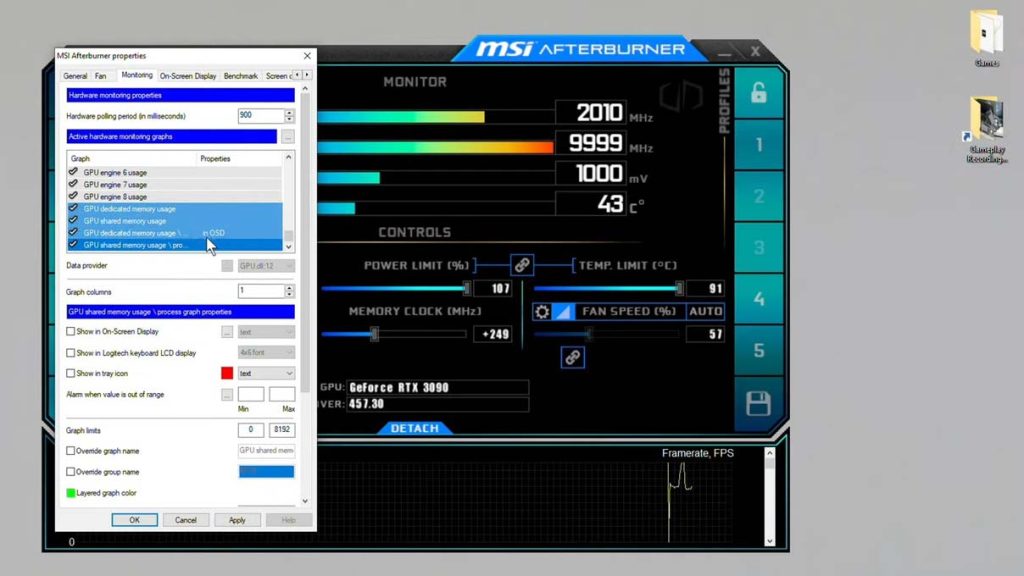
MSI Afterburner
MSI Afterburner is a free utility for MSI graphics cards that shows detailed system stats including VRAM usage.
- Download and install MSI Afterburner
- In Settings, go to Monitoring and enable hardware polling for CPU and GPU
- In-game overlays will now show VRAM usage
GPU-Z
GPU-Z is a free lightweight utility that shows stats about your GPUs including VRAM usage, clock speeds, fan speeds, temperatures etc.
- Download and open GPU-Z
- Check the Graphics Card tab to see dedicated VRAM usage
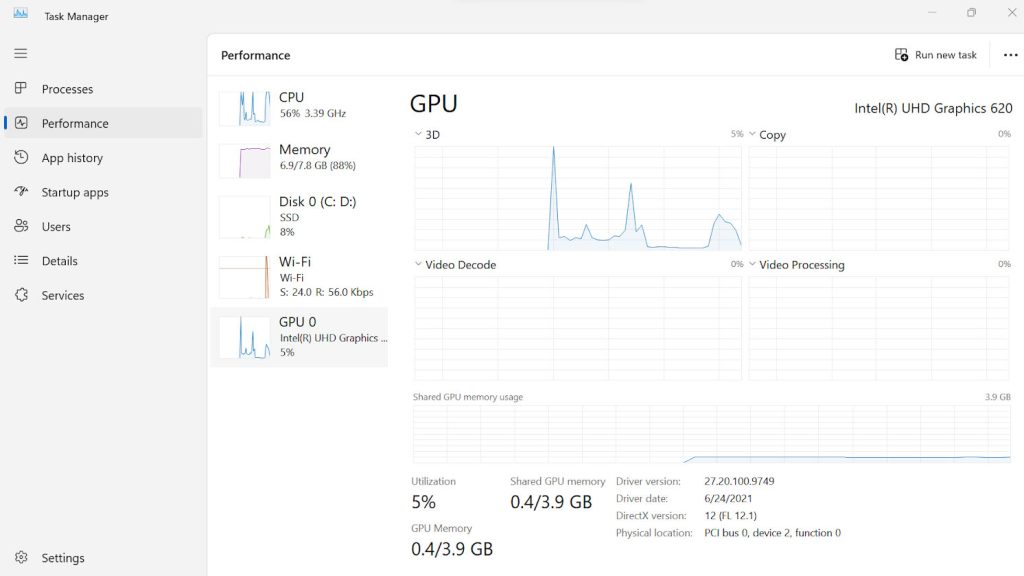
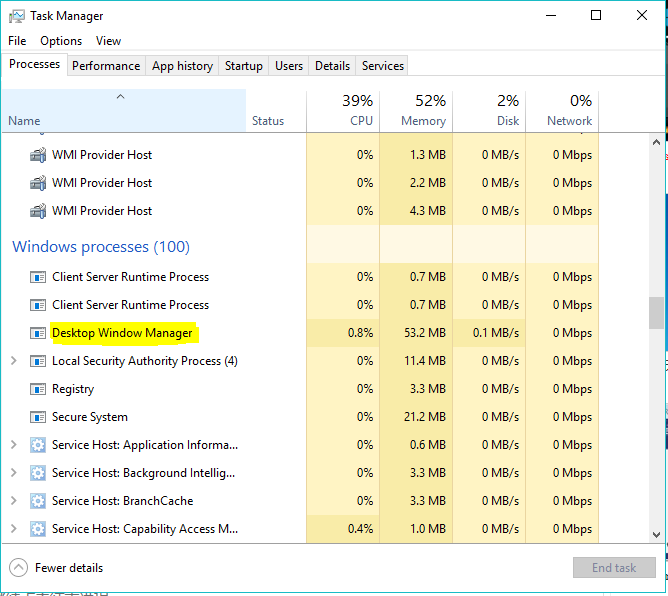
Windows Task Manager
Task Manager in Windows 10 and 11 displays current GPU memory utilization.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager
- Go to the Performance tab
- Check GPU 0 memory to see VRAM usage
Now that you know how to check current VRAM utilization, let’s look at why it might be much higher than expected when your PC is idle.
Why is My VRAM Usage So High When Idle?
There are several common causes for unusually high VRAM usage when your computer is idle and not running any intensive graphics applications:
1. Background Apps and Processes
Many applications continue running background processes even after you close or minimize them. For apps that utilize graphics and VRAM like games, Photoshop, Chrome, etc, their background processes accumulate over time and continue using your VRAM.
For example, if you ran Premier Pro, Photoshop or any video and photo editor apps earlier, its background processes may still be taking up VRAM. The same goes for games launchers, browser tabs, media players and any other apps that handle graphics.
2. Windows Desktop Composition
Windows uses GPU acceleration and VRAM to render desktop elements, visual styles, and composition effects. The more complex your current desktop theme, the more VRAM it requires.
Windows Aero themes and transparency effects utilize more VRAM than basic themes. Changing to a simple desktop theme can help lower idle VRAM usage.
3. Multiple Monitors
Using multiple monitors itself requires more VRAM to manage and store graphical data across all displays.
Additionally, higher resolution monitors demand more VRAM to render sharper images. For instance, a 4K monitor requires 4x the VRAM as a 1080p monitor, even for simple desktop usage.
4. Unoptimized GPU Drivers
Outdated, incorrect or unstable GPU drivers can negatively impact how efficiently your graphics card uses and manages VRAM. Keeping your GPU drivers updated is key to optimize VRAM utilization.
Using older drivers or generic Windows drivers instead of drivers from your GPU manufacturer can also cause inefficient VRAM usage.
5. GPU Architecture and Memory Bandwidth
Certain GPU architectures and memory technologies are better optimized for VRAM usage than others.
Higher memory bandwidth also plays a role in efficient VRAM management. All else being equal, a GPU with 320-bit memory bus will use VRAM more efficiently than one with 128-bit bus.
6. Filed-Up VRAM Caches
Modern GPUs have built-in caches to store frequently accessed data, improving overall performance. But sometimes cached data gets stuck and the VRAM cache fails to clear itself, occupying VRAM.
7. Overclocking
Overclocking your GPU can potentially lead to VRAM getting filled up quicker than intended. This depends on factors like voltages, power limits and VRAM speeds used for overclocking.
Unstable overclocks in particular can cause crashes, freezes and other issues that might appear as high idle VRAM usage.
8. Cryptocurrency Mining
If you’ve used your PC for mining cryptocurrency in the past, mining software sometimes leaves artifacts behind even after uninstalling. These can continue occupying VRAM in the background.
Now that you know the likely reasons, let’s look at how to go about reducing high VRAM usage when idle.
How to Reduce High VRAM Usage When Idle?
Here are some troubleshooting tips and solutions to lower idle VRAM utilization:
Close Unused Apps
Actively close desktop apps and games when you are done using them instead of just minimizing to the taskbar. Background processes from minimized apps can accumulate over time and consume VRAM.
Use Task Manager to monitor and end background processes from apps you are not currently using. Stop web browser processes after closing all tabs as browsers like Chrome and Firefox can leak memory over time.
Limit Startup Apps
Open Task Manager > Startup tab and disable apps that auto-start but are not needed. This prevents unnecessary background processes from loading.
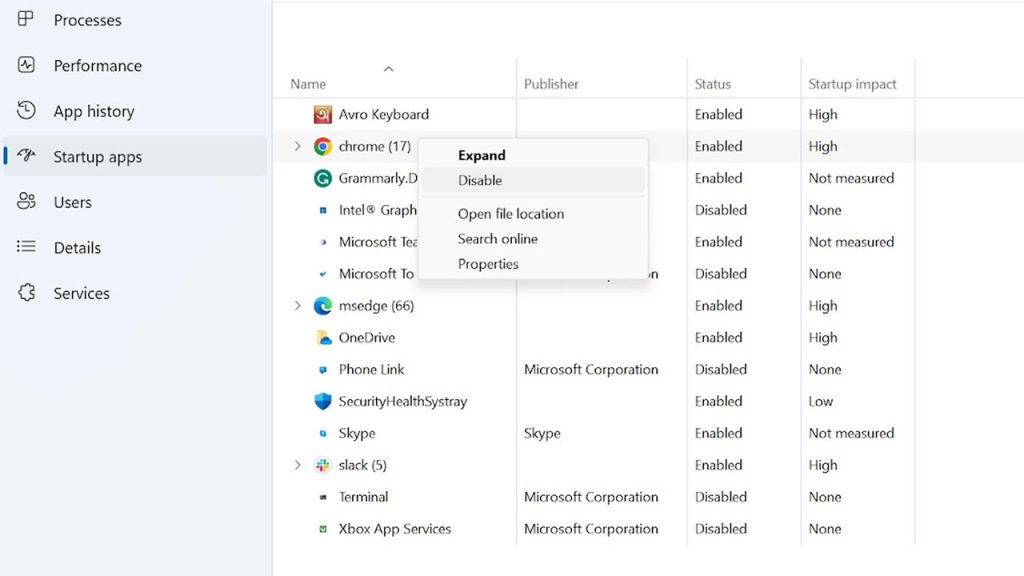
Regularly review and prune your startup app list to minimize startup impact. Common offenders are Steam, RGB lighting apps, game launchers etc.
Some apps have options to disable opening at startup like Chrome, Discord, Spotify – disable auto-start for these if not required.
Update GPU Drivers
Use apps like NVIDIA GeForce Experience or AMD Radeon Software to keep your GPU drivers updated. Updates fix bugs, improve performance and stability.
Always download GPU drivers from your manufacturer’s website, not third party sites. Avoid generic Windows GPU drivers.
DDU (Display Driver Uninstaller) in safe mode can help fully clean previous graphics drivers before installing latest ones.
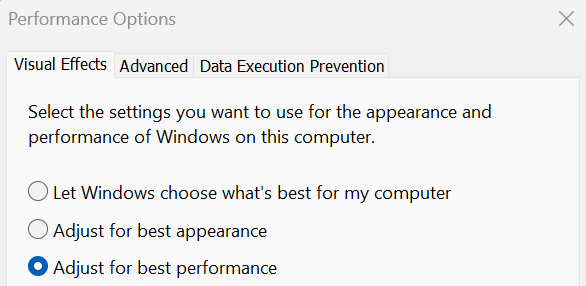
Disable Visual Effects
Visual effects like transparency, animations and Aero themes use GPU resources. Disable them for lower resource usage.
Go to Performance Options > Visual Effects and select “Adjust for best performance” to disable most effects. Alternatively, use a simple Windows theme without transparency effects enabled. The Classic theme works well.
Lower In-Game Settings
Lower in-game resolution, texture quality, anti-aliasing and post-processing effects to reduce VRAM usage.
Disable VSync and FPS caps as they can sometimes cause memory leaks or higher VRAM usage in certain games.
Limit FPS to your monitor’s refresh rate to reduce unnecessary GPU load. Use RivaTuner or in-game FPS limiters.
Disable Hardware Acceleration
Turn off hardware acceleration options in Chrome, Firefox and other browsers. This prevents them from utilizing the GPU and VRAM.
Similarly, disable hardware acceleration in apps like Discord, Spotify etc. from settings if available. Forces them to use CPU instead.
Try disabling Windows Display Capture (WDCS) service to prevent desktop recording features from using VRAM.
Clean VRAM Caches
Use AMD’s vRAM Cleaning Tool or NVIDIA Inspector to periodically clear leftover VRAM allocations and caches. Restarting your PC helps clean VRAM as well.
Shutdown computer instead of Sleep/Hibernate. Uninstall Display Driver using DDU then reinstall latest GPU drivers to fully clear caches.
Scan for Mining Malware
Run a full system scan using Windows Defender Antivirus or paid anti-malware tools to check for crypto mining malware hidden in the background.
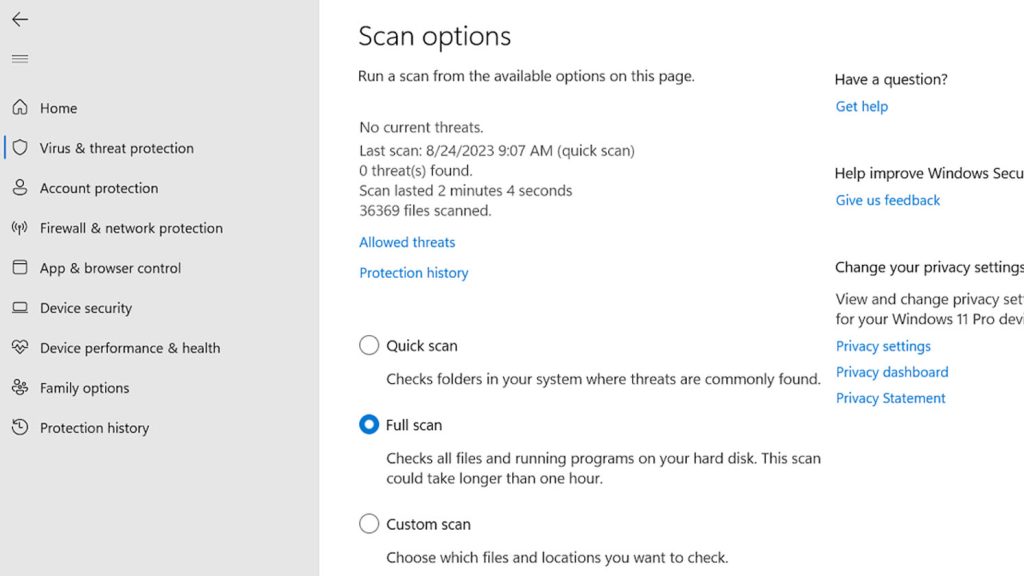
Malwarebytes Anti-Malware is an excellent second opinion scanner for rooting out persistent malware. Check Task Manager for unfamiliar background processes constantly using GPU resources.
Reduce Multiple Monitors
If possible, try reducing your number of monitors down to 1 or 2 high resolution displays instead of 3 or 4 lower resolution ones.
Multiple monitors themselves consume a base amount of VRAM, so fewer monitors helps optimize VRAM use especially for idle usage.
Disable unused monitors instead of just unplugging them. Remaining enabled monitors still reserve VRAM.
Overclock VRAM
Carefully overclocking your graphics cards’ VRAM can increase effective speed and bandwidth which improves performance per watt. However, overclocking does generate extra heat so sufficient cooling is a must.
Avoid excessive voltages beyond manufacturer specs. Memory timing tightening mods can also help optimize VRAM efficiency on some GPUs. But do extensive testing for stability.
These are some of the top solutions for reducing high idle VRAM usage on Windows 10 and 11 PCs. Let’s look at some software tools that can further help optimize VRAM utilization.
Software to Optimize VRAM Usage
Here are a few utilities that can help tweak settings to lower and optimize your overall VRAM usage:
NVIDIA Inspector
NVIDIA Inspector is a powerful free tool for NVIDIA GPUs that lets you monitor and adjust GPU parameters. You can use it to configure and force application-specific VRAM utilization.
RadeonMod
Similar to NVIDIA Inspector but for AMD GPUs, RadeonMod allows adjusting VRAM usage profiles, memory timings, clock speeds and other parameters.
VRAMSizeDX11
VRAMSizeDX11 is a small utility for configuring the amount of VRAM reported to DX11 games. This can help reduce memory leaks and unoptimized VRAM allocation in games.
ISLC
Intelligent standby list cleaner (ISLC) regularly purges unused standby memory to improve system performance and reduce high memory/VRAM usage scenarios.
Process Lasso
Process Lasso offers intelligent CPU and memory optimization including options to force apps to low RAM priority and minimize their memory footprint.
How Much VRAM Do You Need?
Now that you know how to monitor and reduce VRAM usage, a common question is how much VRAM is considered enough?
Unfortunately there is no one-size-fits-all answer. How much VRAM you need depends on your specific usage:
For 1080p gaming – A minimum of 4GB VRAM is recommended, with 6-8GB being the sweet spot. Popular GPUs like the RTX 3060 or RX 6600 provide ample VRAM for smooth 1080p gaming.
For 1440p gaming – You’ll want 6-8GB of VRAM. 8GB or more is recommended if playing visually-demanding games on high settings. RTX 3070 Ti, RX 6700 XT, etc do well here.
For 4K gaming – At least 8GB is recommended, with 10-12GB ideal for higher texture quality and future proofing as games become more VRAM hungry. RTX 3080, RX 6800 XT, etc work great.
For creative work – Video editing, 3D modeling, CAD etc benefit from GPUs with 10-16GB VRAM. NVIDIA Quadro and AMD Radeon Pro cards are popular here.
Multiple monitors – Need more VRAM if running multiple high resolution monitors to handle the increased graphical workload.
So in summary, VRAM needs depend on your graphics workload. Aim for 6-8GB of VRAM for smooth 1080p or 1440p gaming, and 10GB+ for comfortable 4K gaming.
Having more VRAM than needed doesn’t directly improve performance. But insufficient VRAM will cause stutters, low FPS, crashes and other issues.
Is High Idle VRAM Usage Problematic?
You might be wondering if there are any negative effects from having high VRAM usage when your PC is idle.
In most cases, high idle VRAM usage itself is not harmful or problematic. The unused VRAM being occupied is there to be allocated when running graphics intensive software. Think of it as your GPU’s memory reserves.
However in some instances, constantly high VRAM usage when idle can indirectly cause problems:
1. Game Stuttering and Low FPS
When launching games, very high idle usage leaves less free VRAM. This can lead to stuttering, FPS drops or lower texture quality as asset streaming from system RAM is slower.
2. Hanging and Crashes During Rendering
Video editing, 3D modeling and CAD applications need to allocate a lot of VRAM during rendering. Near full usage when idle allows less room for these apps, risking hangs, crashes or failed renders.
3. Thermal Throttling
High VRAM usage generates more heat on some GPUs even when idle. This leads to earlier thermal throttling which reduces clock speeds and performance.
4. Texture Streaming Issues
Textures may appear blurry or be lower resolution if sufficient VRAM isn’t available when loading levels in games that stream assets from storage.
So in general, there is no need to obsess over having high idle VRAM if you aren’t experiencing the above-mentioned problems.
But ideally you want to avoid idle usage consistently staying over 90-95% on a regular basis, as that allows minimal headroom for graphics-intensive apps.
Additional Tips to Manage VRAM Usage
Here are some bonus tips to keep in mind when trying to optimize and reduce VRAM usage on your Windows PC:
- Close GPU monitoring and tweaking utilities when not in use. Many of them occupy VRAM for overlays.
- Disable or lower GPU scheduling in Windows Settings > System > Display if you have an AMD GPU. Can help lower idle usage for some users.
- Change power settings to Optimize for performance instead of battery life or balance modes. This allows the GPU and VRAM to idle down fully.
- Avoid daisy-chaining multiple monitors off one GPU output. Connect monitors directly to GPU ports instead for improved performance.
- Set your BIOS to maximize PCIe lanes for your GPU instead of other slots to avoid bandwidth bottlenecks.
- DDU your GPU drivers in safe mode and do a clean reinstall if you face random spikes in VRAM usage or other anomalies.
- Consider upgrading to a GPU with more VRAM capacity if yours is consistently over 90% utilization even after optimizing.
Conclusion
To summarize, high VRAM usage when your PC is idle is common, caused by various apps, software, and hardware factors. Thankfully there are many troubleshooting steps you can take to reduce and optimize idle VRAM usage.
Consistently having 90%+ VRAM usage when idle risks performance issues when running graphics-intensive software. So aim to keep idle usage below 90% for smooth gaming and stable creative work.
Now you know exactly how to monitor your VRAM usage, why it might be high when idle, and actionable solutions to reduce unnecessary VRAM occupation. Following the tips in this guide will help you optimize idle VRAM usage.
Let us know if you have any other suggestions to minimize idle VRAM usage!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is high VRAM usage always bad?
A: Not necessarily. High VRAM usage only causes issues if it leads to insufficient free VRAM needed by active applications. Idle high usage itself is not harmful as long as you don’t experience problems like stuttering or crashes when gaming or creating content.
Q: Will upgrading GPU or adding more VRAM lower usage?
A: Maybe. More VRAM can help if your current GPU is constantly maxing out its memory capacity. But upgrading without optimizing software and settings won’t fix high VRAM usage causes like memory leaks.
Q: Does RAM affect VRAM usage?
A: Not directly. But with integrated graphics, RAM capacity can limit maximum allocatable VRAM. And for dedicated GPUs, higher system RAM allows VRAM to utilize it as a fallback if needed.
Q: Should I get a GPU with high VRAM just to be safe?
A: Not recommended, as excess unused VRAM doesn’t improve real-world performance. Get a GPU with VRAM suited for your target resolution and workload. Lower capacity GPUs utilized fully are often better than higher VRAM GPUs where the extra memory remains unused.
Q: How can I reduce VRAM usage during gaming?
A: Use lower graphics settings, resolution, install optimization mods, disable unnecessary effects, limit FPS to monitor refresh rate, update GPU drivers, restart game/PC regularly to clear caches.
Q: Does processor/CPU affect VRAM usage?
A: No direct correlation. But a severely outdated/underpowered CPU can bottleneck some GPUs, indirectly causing worse VRAM usage due to the GPU being unable to function at its full potential.
Q: Is it safe to allocate more VRAM via registry edits?
A: Generally not recommended, as forcing higher VRAM without adequate physical memory can cause crashes or freezes. Only modify VRAM allocation if you fully understand the risks and your hardware limits.